Top 5 Things You Should Know About Addyi
Based on each woman’s unique experiences and biological needs, there is a personal definition of what constitutes a “normal period.” However, hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) can be present in women experiencing low sexual desire or libido, causing distress due to a lack of interest in sex.
A woman’s libido can vary over time due to factors such as stress, hormonal changes, and side effects of medications, but these fluctuations are typically short-lived, and desire returns quickly.
According to the Society for Women’s Health Research, HSDD is one of the most common female sexual health issues, affecting one in ten women. The key aspect of female HSDD is a lack of sexual fantasies and desire to engage in sexual activity, resulting in significant distress or interpersonal problems. Fortunately, medications like Addyi are available to address this condition. Keep reading to find out more.
What Exactly Is Addyi?
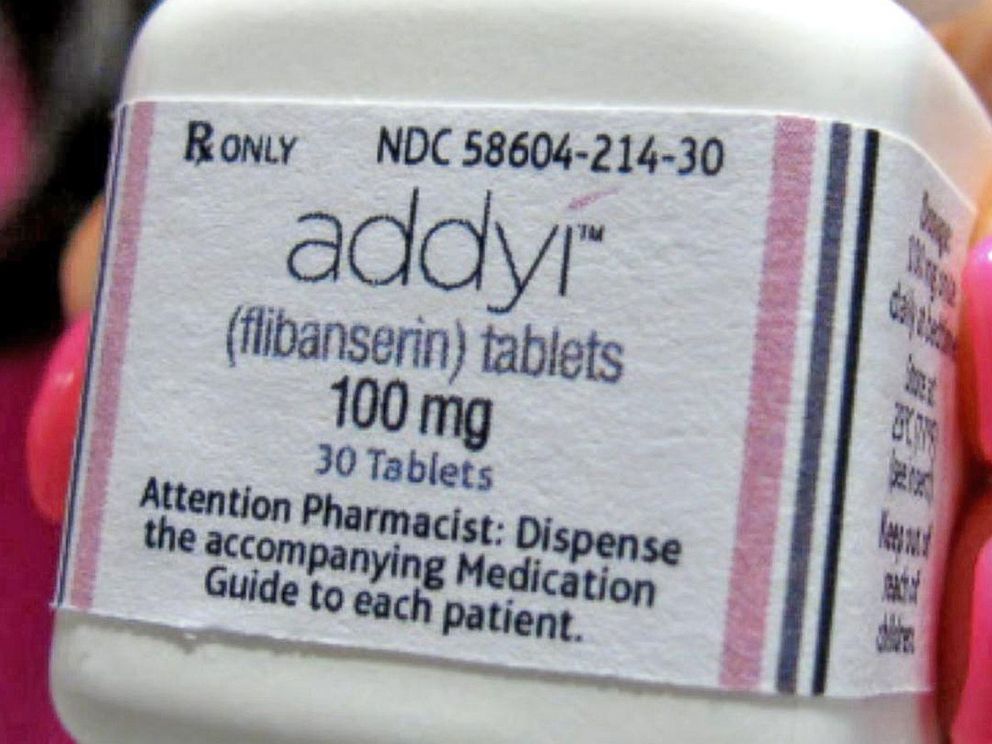
Addyi is a prescription drug for premenopausal women with HSDD that boosts sexual desire while reducing emotional distress. It should only be used when the lack of sexual interest is not caused by physical ailments, mental health issues, relationship problems, substance abuse, or other medications.
While Addyi is often likened to the female equivalent of Viagra, its mechanism of action is quite different. Addyi, by correcting an imbalance of neurotransmitters in the brain that influences sexual desires, functions more like an antidepressant, whereas Viagra enhances blood flow to the genitals.
The medication impacts levels of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine in the brain, and it is taken as a daily tablet before bedtime. Consumption of alcohol while on Addyi is not recommended. People with liver problems or recent alcohol consumption should avoid using Addyi.
Certain medications can have adverse interactions with Addyi. If you are taking any of the following, your doctor may need to adjust your treatment plan:
- Varieties of antifungal medication;
- Specific antibiotics;
- Nefazodone;
- Antiviral medications for hepatitis C or HIV/AIDS.
To ensure the safety of Addyi for you, inform your doctor if you have a history of substance abuse, mental health conditions, low blood pressure, alcoholism, pregnancy, nursing, or if you are under 18 years old.
Below are guidelines on how to use Addyi:
- Follow your doctor’s instructions on dosage and read all provided information.
- Avoid consuming alcohol for at least two hours before and after taking Addyi to prevent a dangerous drop in blood pressure.
- If you feel lightheaded after taking Addyi, lie down if you are not in bed already due to its blood pressure-lowering effects.
- Store Addyi at room temperature away from heat and moisture.
5 Things to Know About Addyi
1. Addyi And Vyleesi For Different Groups Of Women
Both Addyi (flibanserin) and Vyleesi (bremelanotide) are medications used to treat HSDD in premenopausal women. Vyleesi is self-administered as an injectable, while Addyi is taken orally once daily at bedtime.
Addyi – In clinical trials, individuals on Addyi reported more significant improvements in sexual desire, fulfilling sexual encounters, or sexual distress compared to those on a placebo.
Vyleesi – Clinical studies showed that a higher percentage of women on Vyleesi experienced increased sexual desire compared to those on a placebo.
2. Flibanserin Targets HSDD Treatment
Flibanserin, approved by the FDA in 2015, is the first drug designed to treat acquired, global HSDD in premenopausal women. Clinical trials have shown modest improvements in sexual desire, satisfying sexual events, and overall sexual function with this medication.
3. Flibanserin’s Impact on Serotonin
Flibanserin, a multifunctional serotonin agonist and antagonist, enhances sexual interest and desire in premenopausal women by influencing neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin.
The drug targets brain circuits related to libido and acts as an agonist on postsynaptic 5HT1A receptors and an antagonist on 5HT2A receptors to address sexual dysfunction.
4. Hormonal Contraceptives and Side Effects
Combining hormonal contraceptives with Addyi may lead to increased risks of adverse effects. Addyi is recommended for premenopausal women who are likely to use hormonal birth control.
Side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and fatigue were more commonly reported in women using hormonal contraceptives with Addyi, potentially due to increased exposure to the medication.
5. Addyi’s Central Nervous System Effects
Common side effects of Addyi include dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, fatigue, and lowered blood pressure. A sedated state and insomnia are also reported adverse effects.
The central nervous system depressant effects of Addyi may interact with other medications or exacerbate conditions, emphasizing caution and moderation in use.
Addyi is designed as a treatment for HSDD in premenopausal women without prior sexual desire issues and is not intended to enhance sexual performance in menopausal women, men, or children.