Understanding Breast Pain: Common Causes and Management Tips
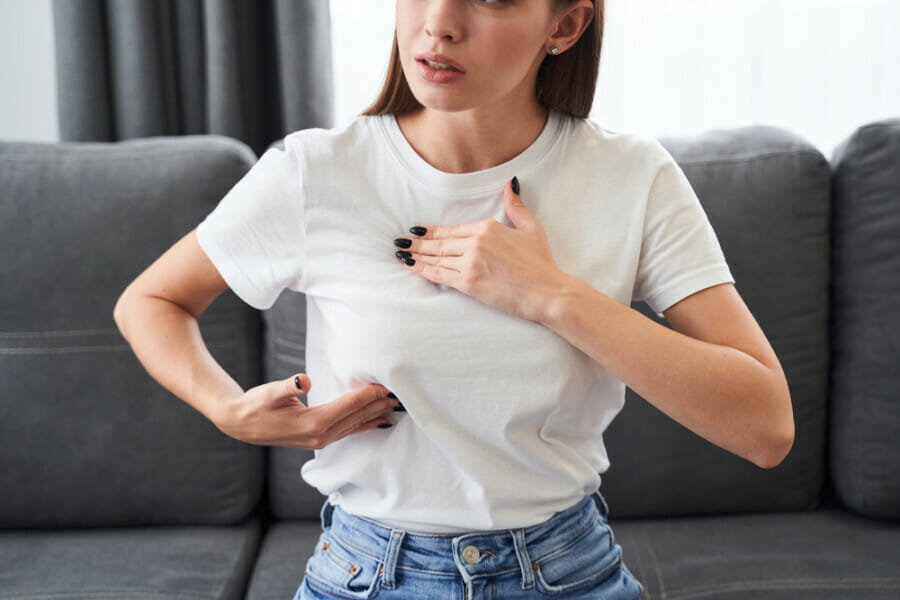
Breast pain, also known as mastalgia, is a frequently reported concern among individuals assigned female at birth (AFAB). It affects about two-thirds of AFAB individuals during their reproductive years, with a higher incidence among those aged 15 to 40. Mastalgia can manifest in various ways, such as heaviness, tightness, swelling, soreness, shooting pains, or burning sensations.
Persistent breast pain can disrupt daily activities and quality of life. It may also cause anxiety about potential underlying health issues like breast cancer. However, it’s essential to note that breast pain, tenderness, or discomfort does not always indicate a serious condition.
Various factors can contribute to mastalgia. Here are five common reasons for breast pain and tips on managing it:
1. Hormonal Changes
Cyclical breast pain, associated with the menstrual cycle, is prevalent among individuals in their 20s, 30s, and approaching menopause. This pain often presents as aching, heaviness, lumpiness, or swelling in both breasts. Hormonal fluctuations, particularly increases in estrogen and progesterone levels, primarily drive this type of mastalgia. To alleviate hormonal-related breast pain, consider:
- Reducing salt intake
- Adopting a low-fat diet temporarily
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Using over-the-counter pain relief
2. Ill-Fitted or Lack of Supportive Bra
Inadequate breast support can strain ligaments, leading to breast soreness and discomfort, especially by the end of the day or during physical activity. It’s crucial to wear a properly fitted, supportive bra to minimize strain and prevent associated aches in the chest, shoulders, neck, and back. Opt for bras that fit comfortably and switch to non-wired options when needed, such as during exercise.
3. Medications
Some medications, including hormone therapies and drugs for hypertension and heart conditions, may cause breast pain as a side effect. If you experience unexplained breast pain, consult your healthcare provider about your medication regimen for further evaluation.
4. Breast Infections
Breast infections, medically termed mastitis, can occur due to exposure to harmful bacteria, commonly affecting breastfeeding individuals. Symptoms may include fever, pain, swelling, redness, and dry, flaky skin. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and pain relief until the infection resolves.
5. Breast Cysts
Breast cysts are fluid-filled lumps that may develop due to fluid accumulation in breast tissue. While most cysts are painless and resolve on their own, they can sometimes cause discomfort. It’s essential to have any unusual breast lumps assessed by a healthcare professional to rule out underlying concerns.
Most cases of mastalgia are manageable, but persistent or severe pain warrants medical attention. Regular breast self-exams and prompt reporting of any changes to your healthcare provider are vital for early detection and peace of mind.